I. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Dioxin contamination in Da Nang airbase
Da Nang airbase locates inside Danang city and neighbors to resident-crowded areas. During the herbicide spraying campaign in Vietnam war, this airbase was used as a storage and place to mix and load the chemicals to spraying equipment. According to the Hatfield report in 2006, total 100,000 barrels (208 1/barrel) of herbicide was stored there, which then were loaded on military C-123 aircraft, helicopter or backpack tank sprayer for spraying in Central of Vietnam. Significant amount of herbicides was spilled over in the airbase platform due to careless of herbicide manipulation in the airbase.
2,3,7,8-TetraCDD congener that contaminated in agent orange was reported with extremely high level in sediment and soil samples which collected from Da Nang airbase in 2006. Dioxins spread to surrounding water bodies and intergrade into food chain, and finally bio-accumulate in human body. Dioxins concentrations in environmental samples are higher than international guideline levels. Congener profile of dioxins indicates that dioxins in Da Nang mainly originates from agent orange and other herbicides. 2,3,7,8-TetraCDD contributes more than 90% of TEQ in samples collected in mixing and loading areas inside the airbase. Highest TEQ level was reported as 365,000 ppt, which was about 365 times higher than the threshold 1,000 ppt of guideline (ATSDR, 1997) and 99% contributed from 2,3.7,8-TetraCDD (361,000 ppt). Da Nang airbase, therefore, was considered as a hot spot of dioxin contamination in Vietnam.
Dioxins in contaminated soils was absorbed in dust particles and flowed into lakes nearby. Fishes and aquatic animals living in these lakes became contaminated with dioxins. Dioxins transferring from environment to food chain and into human body directly relate to the usage of agent orange of US Army during the Vietnam war. As a result, dioxin exposure may cause human health effects.
1.2 Dioxin contamination in Bien Hoa airbase
Among three dioxin-contaminated airbases in Vietnam, Bien Hoa airbase stored the greatest amount of herbicides. There were over 98,000 tanks (45 gallons) of agent orange, 45,000 tanks of agent white and 16,000 tanks of agent blue were stored there (US DOD, 2007). Previous studies showed high levels of dioxins in environmental samples that collected in Bien Hoa airbase (Schecter 2001, 2002). Dioxin from the airbase was spread into surrounding areas, causing contaminations in environment around the airbase. Bien Hoa airbase locates inside a city with condensed populations therefore, dioxin contamination is a serious public concern and need urgent studies and policies to solve the problems.
1.3 Aims of study
The study \"Estimations of chemical/dioxin exposure in soldiers and solutions for protecting soldiers’ health in Bien Hoa, Da Nang, and Phu Cat airbases\" was performed from 2017 - 2019 to provide systematic and basic information for remediation and intervention of dioxin problems in Vietnam. In this presentation, we focus on the health conditions of workers in Bien Hoa, Da Nang, and Phu Cat airbases.
II. METHODS
2.1 Study design
This is a cross-sectional study.
2.2 Study areas
Three dioxin-contaminated airbases including Bien Hoa, Da Nang, and Phu Cat, and one control airbase (Sao Vang) were chosen for this study.
2.3 Subjects
Total 765 subjects who were working in Bien Hoa, Da Nang, Phu Cat, and Sao Vang airbases were recruited for the study. Selection criterions: 1) Agree to participate; 2) Work in airbases for a period of at least one year (still working/retired); 3) Take priority for people suffering one of 17 dioxin-related diseases.
The subjects were invited to health centers in each airbase. A fasting blood sample was collected in the morning, from 7 - 11 AM for determining the biochemical blood indexes.
Basic information such as age, education, smoking, drinking was interviewed by trained staffs.
Informed consents were got from all subjects. The study was accepted by an Ethic Committee for Biomedical study of Vietnam Military Medical University (No. 2061/QĐ-Vietnam Military Medical University).
III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 1. Characteristics of subjects
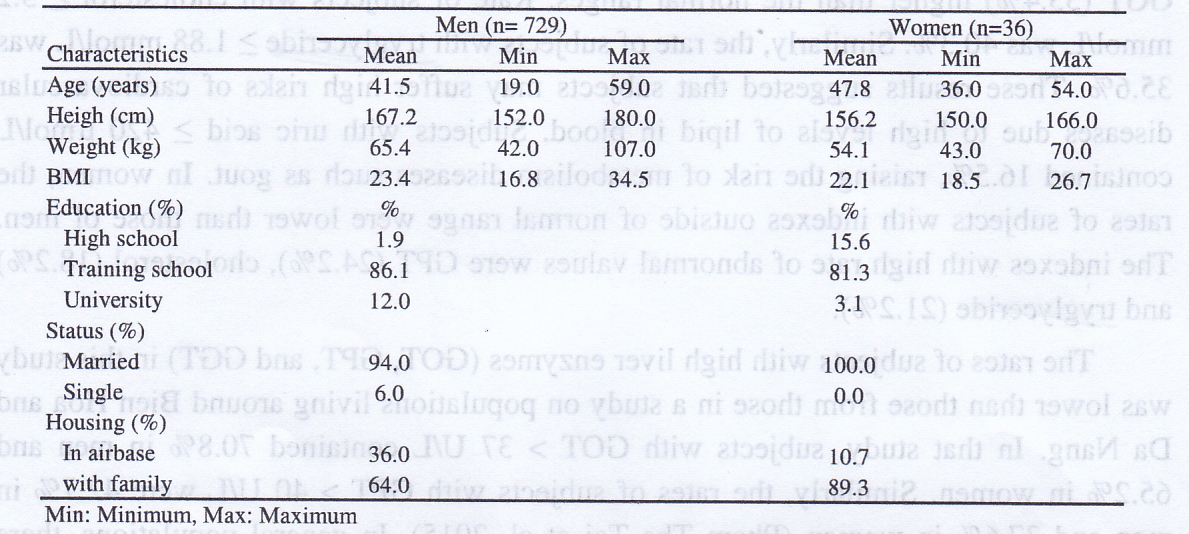 |
Table 1 showed characteristics of the subjects which divided into male group (729) and female group (36). Average ages of men and women were 41.5 and 47.8, respectively. Almost of subjects graduated from training school. In men, 94% was married and 64% was staying with their families. In women, 100% of them was married and almost of them (89.3%) were staying with families.
Table 2. Rate of abnormal blood biochemistry test
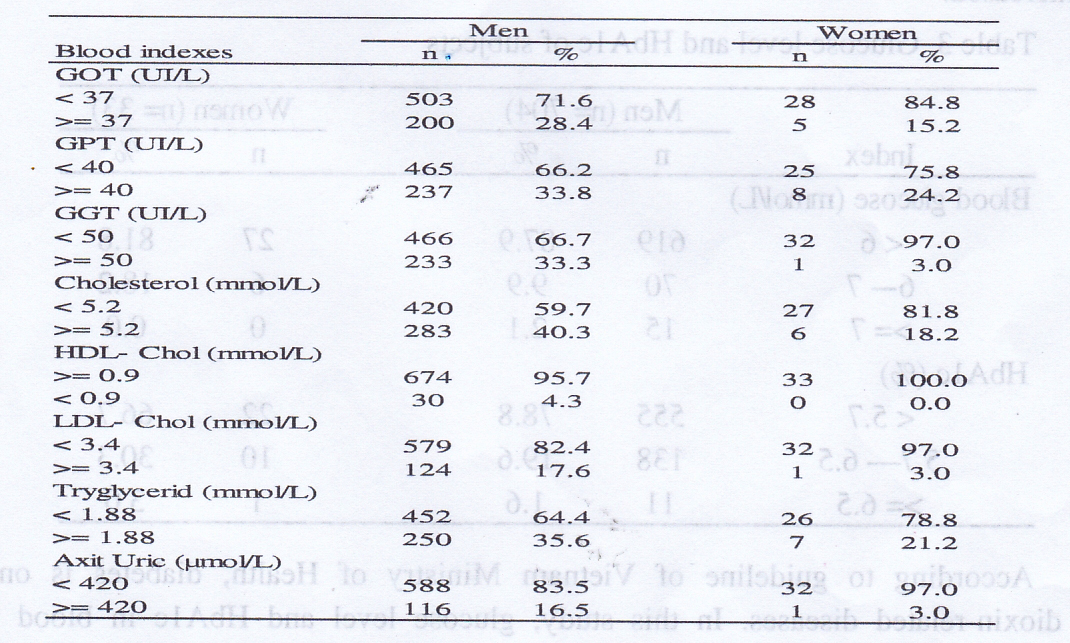 |
Table 2 showed indexes of biochemistry test in blood of male and female groups. Subjects were stratified into subgroups that indexes were within and outside of the normal ranges for GOT, GPT, GGT, cholesterol, HDL-C, LDL-C, triglyceride, uric acid. In men, approximately 1/3 of subjects showed GOT (28.4%), GPT (33.8%) and GGT (33.4%) higher than the normal ranges. Rate of subjects with cholesterol ≥ 5.2 mmol/L was 40.3%. Similarly, the rate of subjects with triglyceride ≥ 1.88 mmol/L was 35.6%. These results suggested that subjects may suffer high risks of cardiovascular diseases due to high levels of lipid in blood. Subjects with uric acid ≥ 420 µmol/L contained 16.5%, raising the risk of metabolism diseases such as gout. In women, the rates of subjects with indexes outside of normal range were lower than those of men. The indexes with high rate of abnormal values were GPT (24.2%), cholesterol (18.2%) and triglyceride (21.2%).
The rates of subjects with high liver enzymes (GOT, GPT, and GGT) in this study was lower than those from those in a study on populations living around Bien Hoa and Da Nang. In that study, subjects with GOT > 37 U/L contained 70.8% in men and 65.2% in women. Similarly, the rates of subjects with GPT > 40 U/L were 42.7% in men and 37.6% in women (Pham The Tai et al, 2015). In general populations, there were certain rates of abnormal liver enzymes, which are from 0.5 - 9% depending on each kind of liver enzymes (Simpson MA, 2015). Liver have functions that to metabolize internal and external toxins in human body. Therefore, this organ is vulnerable to chronicle environmental intoxications, including agent orange/dioxins. These results suggested that liver cells may be damaged that causing such enzymes to be increased.
Table 3. Glucose level and HbAlc of subjects
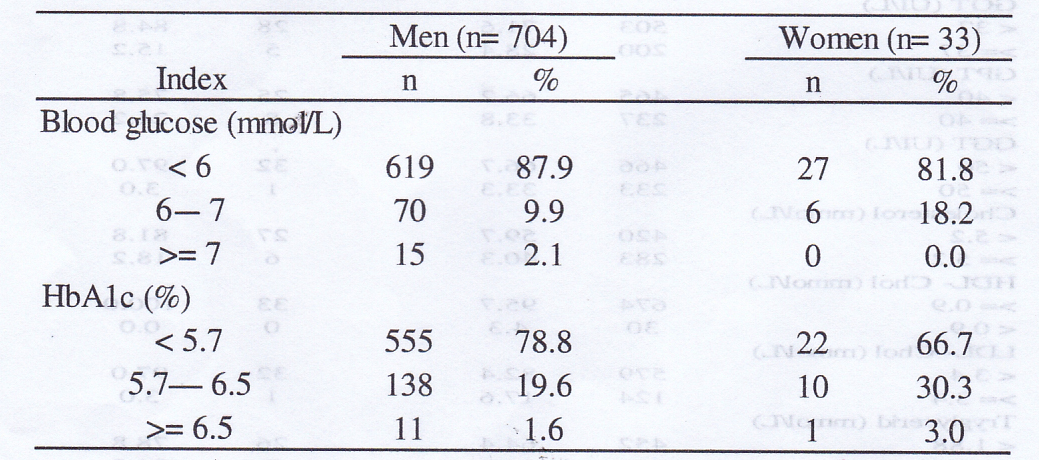 |
According to guideline of Vietnam Ministry of Health, diabetes is one of 17 dioxin-related diseases. In this study, glucose level and HbAlc in blood were measured. In men, the rates of subjects with glucose level from 6 - 7 mmol/L (prediabetes) and ≥ 7 mmol/L (diabetes) were 9.9% and 2.1%, respectively. HbAlc index reflecting pre-diabetes (5.7 - 6.5%) was 19.6% and diabetes ≥ 6.5%) was 1.6%. In women, the rates of abnormal values of glucose and HbAlc tends to be higher than those in men. There were 18.2% of subjects showing glucose level indicating prediabetes and 30.3% of subjects showing HbAlc indicating prediabetes. However, number of subjects in female group was small (33), therefore, larger epidemiology study need to clarify the risk of diabetes in women working in these airbases.
IV. CONCLUSION
The rates of subjects working in the airbases with abnormal values of liver enzymes (GOT, GPT, GGT), cholesterol and triglyceride in men and glucose level and HbAlc in women were high. In future, it is necessary to determine dioxin levels, hormone levels and cancer markers in these subjects to clarify the relationship between dioxin exposure and health damages.
REFERENCES
- Phạm Thế Tài, Đỗ Minh Trung, Nguyễn Văn Long, Nguyễn Tùng Linh, Hoàng Văn Lương. Đánh giá tình trạng sức khỏe của người dân sinh sống tại khu vực ô nhiễm dioxin thuộc thành phố Đà Nẵng và Biên Hòa. Vietnam Journal of Physiology 19(4) 12/2015: 68-74.
- ATSDR. (1997) Interim Policy Guideline: Dioxin and dioxin-like compounds in soil. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service. Atlanta, GA. P10.
- Hatfield. (2009) Comprehensive Assessment of Dioxin Contamination in Da Nang Airport, Viet Nam: Environmental Levels, Human Exposure and Option for Mitigating Impacts.
- Hatfield (2011). Environmental and human health assessment of dioxin contamination at Bien Hoa airbase, Vietnam. [Online]. Available from:URL: http://www.hatfieldgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/AgentOrangeReports. [cited in 2015 October 1st].
- Schecter, A., L.C. Dai, O. Pa¨ pke, J. Prange, J.D. Constable, M. Matsuda, V.D. Thao, and A.L. Piskac. 2001. Recent dioxin contamination from Agent Orange in residents of a Southern Vietnam city. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 43: 435-43.
- Schecter, A., M. Pavuk, J.D. Constable, L.C. Dai, and O. Pa¨ pke. 2002. A follow-up: High level of dioxin contamination in Vietnamese from Agent Orange, three decades after the end of spraying. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 44: 218-20.
- Simpson MA, Freshwater DA. (2015) The interpretation and management of abnormal liver function tests. J R Nav Med Serv 101(1):74-79.
- US DOD (US Department of Defence). 2007. Presentation made at the Second Agent Orange and Dioxin Remediation Workshop, Ha Noi, Vietnam.June 18-19, 2007.
Pham The Tai[1]; Phan Van Manh1; Nguyen Minh Phuong1; Do Minh Trung1; Nguyen Van Long1; Nguyen Tung Linh1; Nguyen Van Khoi1; Hoang Van Luong1.
[1] Vietnam Military Medical University

































Comment